Database Study Design
As leaders in generating real-world evidence from secondary sources of real-world data, we craft study designs which make best use of the capabilities of existing health data.
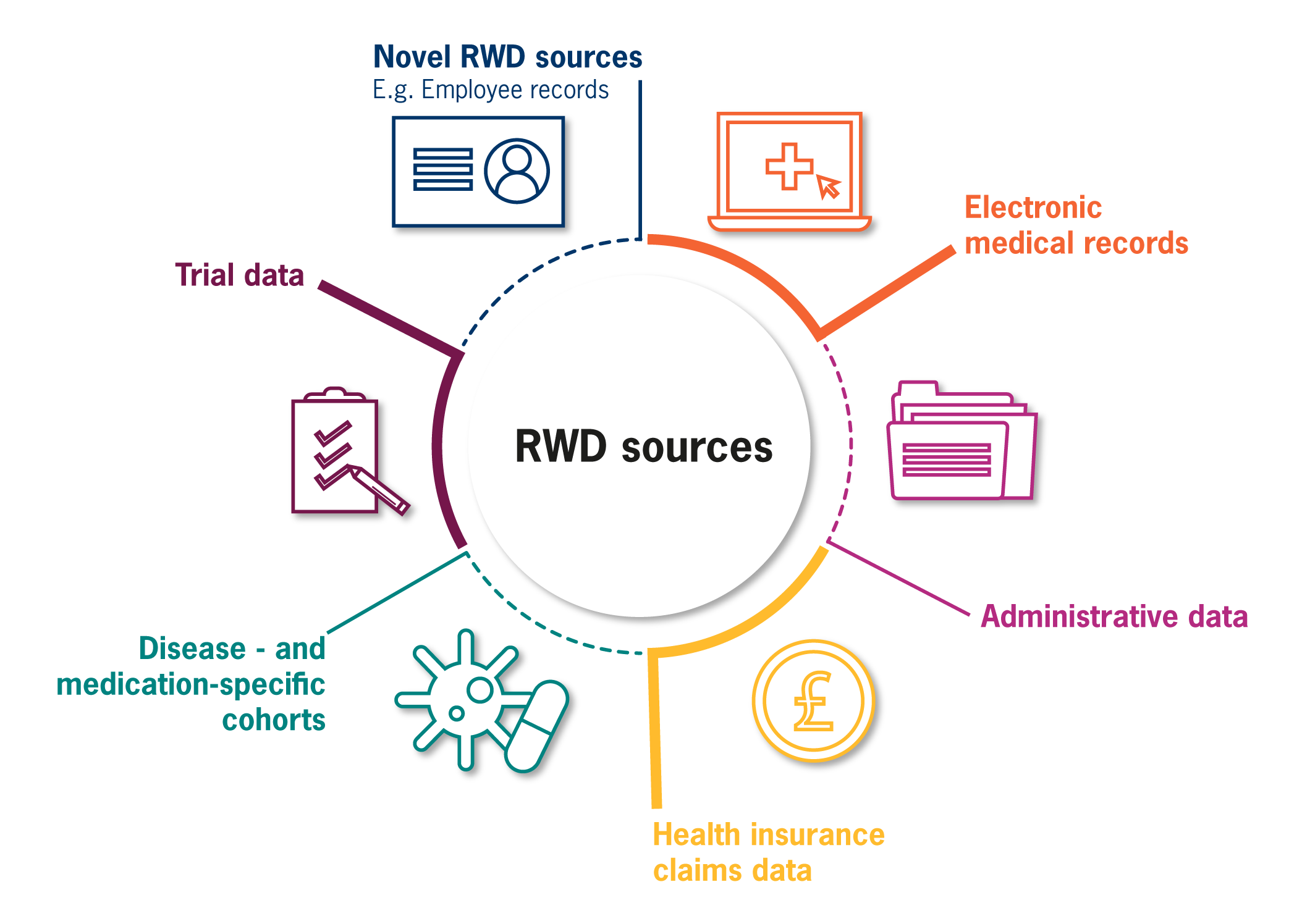
GLOBAL RWD REACH
We have accessed and analysed a multitude of distinct RWD sources across Europe, Asia-Pacific and North America, encompassing a broad range of data types. Consequently, we are cognisant of various data governance models and can draw on our experiences to successfully navigate data access requirements, thus opening up a world of secondary data sources.
In addition, we can access hard to reach sources of RWD through our network of established data partnerships, which we continue to expand worldwide to facilitate indirect access and broaden our coverage of RWD that can be used to address a multitude of RWE needs.
Furthermore, we provide industry-leading support to identify sources of RWD which are best suited to our clients’ evidence needs, led by our command of in-depth internal knowledge held on thousands of sources of secondary data worldwide. By combining this powerful library of RWD sources with our experience of generating effective evidence, we ensure the most optimal RWD source is selected to maximise value and achieve clients’ research goals.
GLOBAL RWD REACH
We have accessed and analysed a multitude of distinct RWD sources across Europe, Asia-Pacific and North America, encompassing a broad range of data types. Consequently, we are cognisant of various data governance models and can draw on our experiences to successfully navigate data access requirements, thus opening up a world of secondary data sources.
In addition, we can access hard to reach sources of RWD through our network of established data partnerships, which we continue to expand worldwide to facilitate indirect access and broaden our coverage of RWD that can be used to address a multitude of RWE needs.
Furthermore, we provide industry-leading support to identify sources of RWD which are best suited to our clients’ evidence needs, led by our command of in-depth internal knowledge held on thousands of sources of secondary data worldwide. By combining this powerful library of RWD sources with our experience of generating effective evidence, we ensure the most optimal RWD source is selected to maximise value and achieve clients’ research goals.
Scientifically rigorous and credible research
Our clients trust us to generate and deliver evidence used for a broad variety of purposes, including health technology assessments, health economic modelling, scientific publications and building clinical awareness.
We design our studies with the end-goal in mind and support our clients to communicate the evidence effectively, most frequently through peer-reviewed journal articles and conference presentations.
Scientifically rigorous and credible research
Our clients trust us to generate and deliver evidence used for a broad variety of purposes, including health technology assessments, health economic modelling, scientific publications and building clinical awareness.
We design our studies with the end-goal in mind and support our clients to communicate the evidence effectively, most frequently through peer-reviewed journal articles and conference presentations.
End-to-end service
We provide consultancy and support throughout the lifecycle of a study, from conceptualisation and design through to implementation and dissemination. Each study has a core team and consistent point of contact from the outset until completion. A key focus of our team is to build long-term productive relationships with our clients; we believe it is in such deep collaborations that the most effective research is conducted.
We also offer modular support, employing our specialist skills to complement existing capabilities or address resourcing or knowledge gaps within our clients’ research teams.
Preliminary research
– Feasibility assessments
– Literature searches with systematic collation of data
– Initial contact with data custodians
Study kick-off
– Study design and planning
– Building a collaborative partnership with our clients
– Hosting steering committees
Protocol and SAP
– Detailed comprehensive protocol and statistical analysis plan (SAP)
study documents
– Clinically-informed development of medical code lists
Data access
– Preparation
and support with data application
– Liaison with data custodians
– Contracting and
sub-licensing
Analysis and interpretation
– Dedicated
secondary data specialist analysts
– Thorough quality control procedure
Dissemination
– Full technical report
– External and internal presentation preparation and delivery
– Publication medical writing and submission support
End-to-end service
We provide consultancy and support throughout the lifecycle of a study, from conceptualisation and design through to implementation and dissemination. Each study has a core team and consistent point of contact from the outset until completion. A key focus of our team is to build long-term productive relationships with our clients; we believe it is in such deep collaborations that the most effective research is conducted.
We also offer modular support, employing our specialist skills to complement existing capabilities or address resourcing or knowledge gaps within our clients’ research teams.
Preliminary work
– Feasibility assessments
– Literature searches with systematic collation of data
– Initial contact with data custodians
Study kick-off
– Study design and planning
– Building a collaborative partnership with our clients
– Hosting steering committees
Protocol and SAP
– Detailed comprehensive protocol and statistical analysis plan (SAP)
study documents
– Clinically-informed development of medical code lists
Data access
– Preparation
and support with data application
– Liaison with data custodians
– Contracting and
sub-licensing
Analysis and interpretation
– Dedicated
secondary data specialist analysts
– Thorough quality control procedure
Dissemination
– Full technical report
– External and internal presentation preparation and delivery
– Publication medical writing and submission support
AN EFFECTIVE BLEND OF EXPERTS
We believe our team of epidemiologists, health economists, biostatisticians, data scientists, clinical experts and programmers is unparalleled in its combination of skills, experiences and backgrounds. It is from this strength that we produce high-quality research using secondary RWD.
Each research need is carefully considered to ensure the relevant skillsets of our team are leveraged to deliver success. This core study team then brings in specific expertise where appropriate throughout the study, including from therapy area specialists who sit in ARW’s Disease Specific Programme teams.
DEDICATED IN-HOUSE ANALYTICS
We have a specialist team of statistical programmers dedicated to working with secondary RWD sources, trained on the manipulation and analysis of such data to produce meaningful outputs. We believe our statistical programmers’ understanding of the fundamental data collection, underlying structure, relational model, data fields and coding systems for each RWD source is essential to using the data source effectively and extracting valuable insights. These experts are fully integrated into the core study teams on every project, providing statistical input at every stage from study design to evidence dissemination.
Our team are well versed in translating research questions into practical data analysis methods and applying a wide variety of both conventional and more innovative statistical techniques to analysis of secondary RWD.
AN EFFECTIVE BLEND OF EXPERTS
We believe our team of epidemiologists, health economists, biostatisticians, data scientists, clinical experts and programmers is unparalleled in its combination of skills, experiences and backgrounds. It is from this strength that we produce high-quality research using secondary RWD.
Each research need is carefully considered to ensure the relevant skillsets of our team are leveraged to deliver success. This core study team then brings in specific expertise where appropriate throughout the study, including from therapy area specialists who sit in ARW’s Disease Specific Programme teams.
DEDICATED IN-HOUSE ANALYTICS
We have a specialist team of statistical programmers dedicated to working with secondary RWD sources, trained on the manipulation and analysis of such data to produce meaningful outputs. We believe our statistical programmers’ understanding of the fundamental data collection, underlying structure, relational model, data fields and coding systems for each RWD source is essential to using the data source effectively and extracting valuable insights. These experts are fully integrated into the core study teams on every project, providing statistical input at every stage from study design to evidence dissemination.
Our team are well versed in translating research questions into practical data analysis methods and applying a wide variety of both conventional and more innovative statistical techniques to analysis of secondary RWD.
Case studies
Comparative Effectiveness of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol versus Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting β2-Agonist in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in a Primary Care Setting in England
Evidence need:
Recommended initial maintenance therapy for COPD include long-acting agents, such as LAMA/LABA or ICS/LABA dual therapy
Real-world evidence comparing the effectiveness of different single inhaler dual therapies, which would help inform treatment decisions, is limited in the UK with existing evidence restricted to randomised controlled trials

Solution:
Three comparative effectiveness research COPD studies using linked UK primary and secondary care data (CPRD-HES)
- Feasibility of comparative effectiveness research studies determined via a published 3-stage pre-study feasibility framework1
- New-user, active comparator, retrospective cohort designs employing IPTW to adjust for measured confounders
Treatment comparisons and primary endpoints of:
-
- UMEC/VI vs. TIO/OLO – Rescue medication use (prescriptions) over 12 months
- UMEC/VI vs. IND/GLY – Rate of moderate-to-severe acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) over 12 months
- UMEC/VI vs. twice daily ICS/LABA – Medication adherence (as measured via the proportion of days covered [PDC]) over 12 months
Superiority and non-inferiority margins were determined based on clinical relevance and existing literature
Key findings:
UMEC/VI demonstrated superiority over TIO/OLO regarding 12-month rescue medication use
Non-inferiority of UMEC/VI vs. IND/GLY was demonstrated on moderate-to-severe AECOPD rate at 6, 12 and 18 months
UMEC/VI was shown to be superior to twice-daily ICS/LABA in medication adherence

Czira A, Requena G, Banks V et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol versus Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting β2-Agonist in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in a Primary Care Setting in England. nt J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Apr;18:643-659.
3x posters (# 2118, 2119, 3619) presented at: ERS; 2022 Sep 4-6; Milan, Italy
1 Requena G et al. Poster #159 presented at: ICPE; 2022 Aug 24-28; Copenhagen, Denmark
COPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; LAMA/LABA – Long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist; ICS/LABA – Inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonist; CPRD – Clinical Practice Research Datalink; HES – Hospital Episode Statistics; IPTW – Inverse probability of treatment weighting; UMEC/VI – Umeclidinium/vilanterol; TIO/OLO – Tiotropium/olodaterol; IND/GLY – Indacaterol/glycopyrronium
Contemporary economic burden in a real-world heart failure population with Commercial and Medicare supplemental plans
Evidence need:
There is a paucity of data on the economic burden of HF by LVEF; namely, for HFrEF and HFpEF patients
Real-world evidence on the HCRU and medical costs of HF management is critical to support the economic value propositions of the client’s asset to US payers

Solution:
A retrospective, longitudinal cohort study of a prevalent HF population in the US via IBM® Watson Health’s Limited Claims-EHR Dataset (MarketScan Commercial and Medicare Supplemental linked to Explorys)
Treatment group at index (HFrEF, HFpEF or HFuEF) was determined by most recently observed LVEF-specific diagnosis:
- Sensitivity analyses were conducted on treatment group assignment to account for conflicting LVEF-specific diagnoses
All-cause and HF-related HCRU and expenditures were reported by service type (inpatient, outpatient, and pharmaceutical), including for HF hospitalisations (hHFs) and urgent HF visits:
-
- Urgent HF visits were defined as emergency department visits with HF as the primary diagnosis, but not constituting an hHF.
- Definitions as per the CDISC were not feasible based on availability/ granularity of data within the study data
Key findings:
HFrEF and HFpEF present sizeable burden on the US healthcare system across a broad age range
Urgent HF visits are important clinical events representing a target for quality improvement
Accurate coding and LVEF-specific diagnosis of patients may also represent an opportunity for improvement in care quality

Lam CSP, Wood R, Vaduganathan M et al. Contemporary economic burden in a real-world heart failure population with Commercial and Medicare supplemental plans. Clin Cardiol. 2021; 44(5): 646-655
LVEF – Left ventricular ejection fraction; HFrEF – HF with reduced EF; HFpEF – HF with preserved EF; HCRU – Healthcare resource use; HFuEF – HF with unknown/ambiguous EF; hHF – HF hospitalisation; CDISC – Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium
Epidemiology and treatment patterns of the patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of real world data in Japan
Evidence need:
Novel pharmacological treatments have been developed for mUC which has a very poor prognosis
Current epidemiological trends and real-world treatment pathways in UC are largely unknown

Solution:
A retrospective, longitudinal cohort study using the HCEI/RWD Co. database (since acquired by JMDC) between Jan-2010 and Mar-2020
- Covers approx. 20 million patients from over 180 private and public medical institutions
Newly diagnosed la/mUC patients were identified via complex algorithmic classification, due to the lack of diagnostic coding for UC, and divided by index tumour site (bladder, ureter, renal pelvis or urethra):
-
- Local coding systems (MEDIS-DC and YJ) were used to identify the patient population and treatments; often mapped to internationally recognized standard coding system codes (e.g. ICD-10 and ATC) to improve accuracy.
Endpoints included prevalence and incidence, treatment pathways and healthcare resource use
Key findings:
Age-adjusted incidence and period prevalence of la/mUC increased from 2015 to 2019, and estimates were high for bladder la/mUC compared with other la/mUC.
Use of GEM+CIT combination therapy decreased with age and advancing lines of therapy compared with GEM+CARB.

Yamamoto O A et al. Oral presentation at: JSCO; 2021 Oct 21-23; Yokohama, Japan
Manuscript in development
HCEI/RWD Co. – Health, Clinic, and Education Information Evaluation Institute/Real World Data Company; DPC – Diagnostic procedure combination; ICD-10 – International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision; ATC – Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical; HCRU – Healthcare resource use; GEM – Gemcitabine; CIS – Cisplatin; CARB – Carboplatin
Living with ulcerative colitis in Germany: a retrospective analysis of dose escalation, concomitant treatment use and healthcare costs
Evidence need:
Despite the importance of effective long-term treatment in UC, treatment changes are observed in substantial numbers of patients
Also a lack of comparative HCRU and cost data regarding the implications of incomplete response to available biologic treatment options – improved understanding of this relationship may help inform UC disease management strategies

Solution:
A retrospective, longitudinal cohort analysis of German statutory health insurance (SHI; Gesetzliche Krankenversicherung) claims data covering approx. 5 million patients and over 50% of German SHIs:
- Data analysis conducted in Germany to confirm with SHI regulations; regular/ close communication and quality control/ review of outputs required to ensure correct interpretation and execution of study protocol, respectively
New users of biologic therapy for UC divided by index treatment: adalimumab, golimumab, infliximab or vedolizumab
Endpoints included biologic therapy dose escalations, concomitant steroid and/or immunosuppressant use, and all-cause and UC-related HCRU and direct medical costs:
- Dose escalations defined as a daily dose increase of ≥50% compared with recommended maintenance dosing
Key findings:
Control with current biologics is suboptimal despite a number of available treatment options; with substantial dose escalations, concomitant medication use and HCRU observed
Novel treatments, or better utilisation of existing treatments, that provide sustained steroid-free remission without the need for dose escalations or concomitant therapies may be warranted

Dignass A, Waller J, Cappelleri JC et al. Living with ulcerative colitis in Germany: a retrospective analysis of dose escalation, concomitant treatment use and healthcare costs. J Med Econ. 2020 Apr;23(4):415-427.
HCRU – Healthcare resource use